What Does Dog Body Language Say? 6 Popular Signs Recognize Your Dog Is Trying to Talk to You

Sharing is Caring!
Introduction
Dog body language is a fascinating and complex system of communication that dogs use to express their thoughts, feelings, and intentions to other dogs and to humans. Understanding and interpreting a dog’s body language is essential for anyone who wants to build a strong and meaningful relationship with their dog, as well as for anyone who works with dogs professionally, such as veterinarians, trainers, and dog groomers.
By learning to recognize and understand the various dog body language signals that they use, we can gain valuable insights into what our dogs are trying to tell us and how we can better meet their needs. In this article, we will take a look at some of the most common dog behavior that they use and what they might be trying to say.
6 Main Signs Help You Understanding Dog Body Language
1. Barking

Dogs bark for a variety of reasons, including to alert their owners to danger, to protect their territory, to get attention, and to express excitement or frustration. Barking is a normal and natural behavior for dogs, and it can serve a valuable purpose in helping to keep dogs and their human families safe. However, excessive barking can be a problem for dogs and their owners, and it is important to understand why a dog is barking in order to address the underlying issue and find a solution.
There are many different types of barking, each with its own distinct characteristics and meanings. Here are a few examples of common types of barking and what they might be trying to say:
- Alarm barking: This type of barking is used by dogs to alert their owners to potential danger or to signal that something out of the ordinary is happening. Alarm barking is usually loud, urgent, and repetitive, and it may be accompanied by other dog body language signals such as a stiff posture, raised hackles, or a forward-leaning stance.
- Play barking: When dogs are having fun and want to play, they may bark in a high-pitched, excited tone. Play barking is often accompanied by other exciting behaviors such as wagging tails, running around, and jumping up.
- Frustration barking: Dogs may bark when they are feeling frustrated or annoyed, such as when they are trying to get something they want but are being prevented from doing so. Frustration barking may be accompanied by other body language signals such as pacing, spinning, or jumping.
- Attention-seeking barking: Some dogs may bark when they want attention from their owners or when they are feeling lonely or neglected. Attention-seeking barking may be accompanied by other attention-seeking behaviors such as pawing or nosing.
2. Whining or Whimpering

Dogs may whine or whimper when they want something, such as food, water, attention, or to go outside. They may also whine or whimper when they are feeling distressed or uncomfortable, such as when they are in pain, scared, or anxious. Whining or whimpering can be dog body language to communicate their needs or to seek comfort and reassurance from their owners.
Here are a few examples of situations in which a dog might whine or whimper and what they might be trying to communicate:
- Hunger or thirst: Dogs may whine or whimper when they are hungry or thirsty, especially if they are used to being fed or given water at a certain time.
- Attention-seeking: Some dogs may whine or whimper when they want attention from their owners, such as when they are feeling lonely or left out.
- Need to go outside: Dogs may whine or whimper at the door or at their owner’s feet when they need to go outside to go to the bathroom or for a walk.
- Distress or discomfort: Dogs may whine or whimper when they are feeling distressed or uncomfortable, such as when they are in pain, scared, or anxious. This can be a sign that something is wrong and that the dog needs help or reassurance.
3. Growling
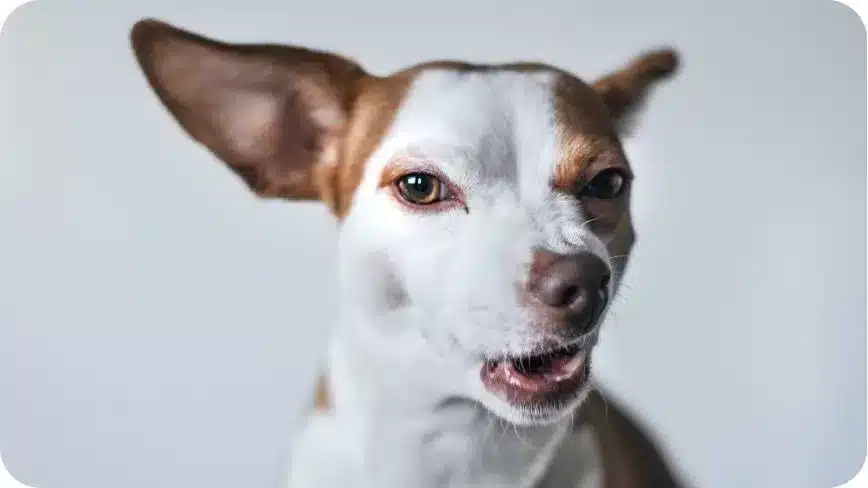

Growling is a form of communication that dogs use to express their feelings of anger, aggression, or dominance. Understanding and interpreting dog body language, including their growling. Growling can be a sign that a dog is feeling threatened or annoyed and that they are prepared to defend themselves if necessary. Growling can also be a way for dogs to assert their dominance over other dogs or to establish their place in the social hierarchy. However, it is also important to understand that growling is not always a sign of aggression and that it can have different meanings depending on the context in which it occurs.
Here are a few examples of situations in which a dog might growl and what they might be trying to communicate through their body language:
- Threatened or annoyed: Dogs may growl when they feel threatened or annoyed, such as when they are approached by an unfamiliar person or animal
- Territorial or protective: Dogs may growl to protect their territory or to defend their family or belongings. This can be a sign that a dog is feeling territorial or protective and that they are prepared to defend their space if necessary. Other dog body language signals to look for in this context might include a stiff posture, raised hackles, or a forward-leaning stance.
- Dominant dog: Dogs may growl to assert their dominance over other dogs or to establish their place in the social hierarchy. This can be normal and natural behavior, especially among pack animals like dogs, but it is important to intervene if the growling becomes aggressive or out of control. Other body language signals to look for in this context might include a stiff posture, raised hackles, or a forward-leaning stance.
4. Tail Wagging
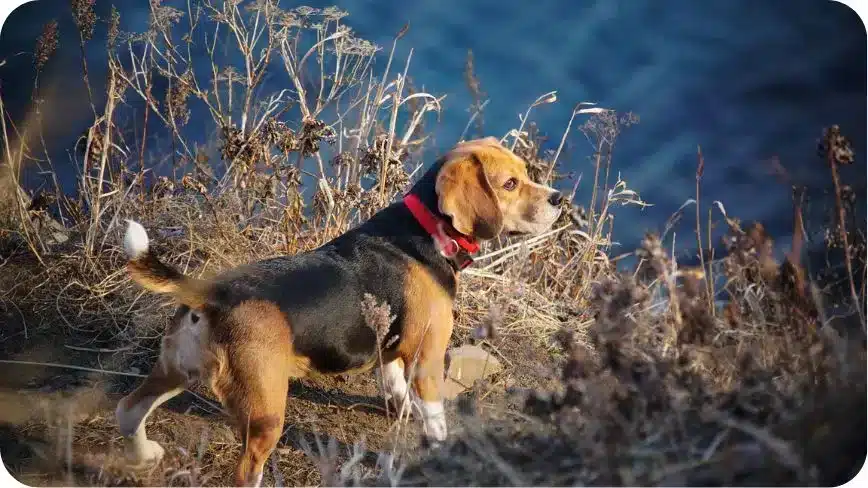

The movement of a dog’s tail is an important aspect of dog body language and can provide valuable clues about their mood or intention. . A wagging tail can be a sign that a dog is happy, excited, or playful, but it can also indicate other emotions or intentions depending on the context in which it occurs and the other dog behavior signals the dog is using.
Here are a few examples of different types of tail wagging and what they might be trying to communicate through their body language:
- Happy or excited: A wagging tail that is held high and wagged in a comprehensive, sweeping motion is often a sign that a dog is feeling happy or excited. This type of tail wagging is usually accompanied by other dog behavior signals such as a relaxed posture, a wiggling body, and a happy facial expression.
- Playful: When dogs are feeling playful and want to play, they may wag their tail in a more energetic and rapid fashion. This type of tail wagging is often accompanied by other playful behaviors such as running around, jumping up and barking.
- Anxious or uncertain: A tail that is wagged low or in a hesitant or subdued manner can be a sign that a dog is feeling anxious or uncertain. This type of tail wagging may be accompanied by other dog behavior signals such as a tense posture, averted gaze, or flattened ears.
- Aggressive: A tail that is held high and wagged stiffly or rapidly can be a sign that a dog is feeling aggressive or dominant. This type of tail wagging is often accompanied by other aggressive body language signals such as a stiff posture, raised hackles, and a forward-leaning stance.
5. Pawing or Nudging
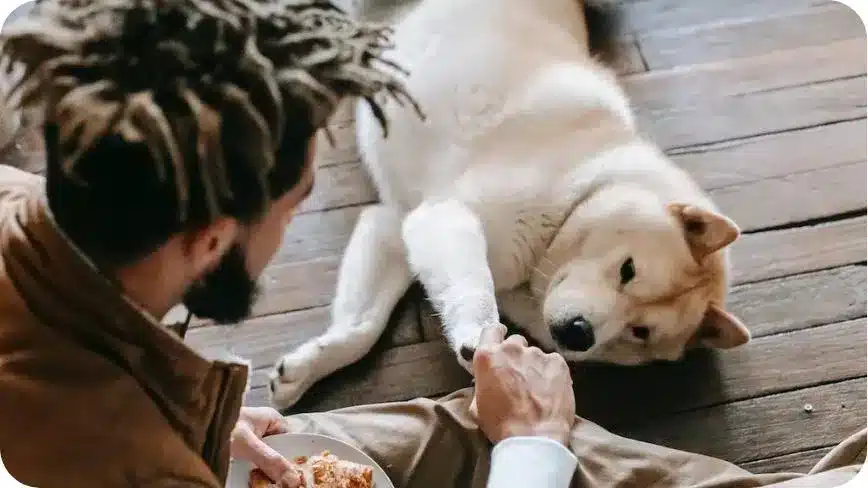

Pawing or nudging is one form of communication that dogs use to get attention, signal their needs or desires, or express affection.
Here are a few examples of situations in which a dog might paw or nudge and what they might be trying to communicate through their body language:
- Attention-seeking: Some dogs may paw or nudge their owners when they want attention, such as when they are feeling lonely or left out. This type of pawing or nudging is often accompanied by other attention-seeking behaviors such as barking or whining.
- Needing something: Dogs may paw or nudge their owners or certain objects when they want something, such as food, water, or to go outside. This type of pawing or nudging is often accompanied by other dog behavior signals such as looking at the object or person they want or making vocalizations.
- Affection: Dogs may paw or nudge their owners or other people as a way of expressing affection or seeking comfort. This type of pawing or nudging is often accompanied by other dog body language about affectionate behaviors such as licking or snuggling
6. Making Eye Contact

Eye contact can be a way for dogs to communicate their feelings, show dominance or submission, or establish a bond with other dogs or with humans.
Here are a few examples of situations in which a dog might make prolonged eye contact and what they might be trying to communicate through their body language:
- Dominance: Dogs may make prolonged eye contact as a way of showing dominance or as a challenge to other dogs. This type of eye contact is often accompanied by other dominant dog body language signals such as a stiff posture, raised hackles, and a forward-leaning stance.
- Submission: Dogs may make prolonged eye contact as a way of showing submission or as a sign of respect to other dogs or to humans. This type of eye contact is often accompanied by other submissive dog behavior signals such as a lowered body posture, averted gaze, and a wagging tail.
- Bonding: Dogs may make prolonged eye contact as a way of establishing a bond with other dogs or with humans. This type of eye contact is often accompanied by other bonding behaviors such as licking or snuggling.
Conclusion
In summary, there are many ways that dogs try to communicate with humans through their body language. Some of the main signs to look for include barking, whining or whimpering, growling, tail wagging, pawing or nudging, and making eye contact. By paying attention to and interpreting a dog’s body language, it is possible to get a better understanding of what they are trying to communicate and to strengthen the bond between humans and dogs.
Understanding and interpreting a dog’s body language is essential for anyone who wants to build a strong and meaningful relationship with their dog. By paying attention to the context in which a dog is using certain body language signals and by looking for patterns and consistencies in their behavior, it is possible to get a good idea of what a dog is trying to communicate.
In conclusion, paying attention to dog body language is an important part of building a strong and meaningful relationship with them. By understanding what a dog is trying to communicate through their body language, it is possible to strengthen the bond between humans and dogs and to create a deeper understanding and connection with our canine companions.
Sharing is Caring!
About The Author
PawCool Team
Related Categories: Dog Stories | Dogs
Latest Articles

Never Miss A Thing!
All pet stories & guides you care about